Понимание стальных профилей и их применения
Что означают профили C, Z и H в современном строительстве
Сегодня стальные профили, обычно известные как секции C, Z и H, являются основой большинства современных конструктивных и солнечных систем монтажа. Таким образом, геометрия каждого профиля и механическое поведение определяют, как распределяются нагрузки, как делаются соединения и какими способами материалы эффективно работают в течение длительного времени.
С-профили или каналы ценятся тем, что легкие, но сильные. Z-профили перекрываются, чтобы создать более длинные расстояния без потери жесткости. H-секции, самые тяжелые и жесткие, справляются с фундаментальными и промышленными нагрузками, которые не могут выполнять меньшие профили. Выбор из них определяет общую безопасность, долговечность и стоимость стальной конструкции.
Почему выбор формы стали важен для солнечной монтажи и промышленных рам
При солнечной монтаже и промышленной раме выбор профиля является не только конструктивным, но и коммерческим решением. Правильная форма стали улучшает скорость установки, уменьшает материальные отходы и обеспечивает стабильность в региональных условиях ветра или снега. Неправильная геометрия может увеличить напряжение в точках соединения и сократить срок службы.
Профильная сталь: легкий и универсальный выбор
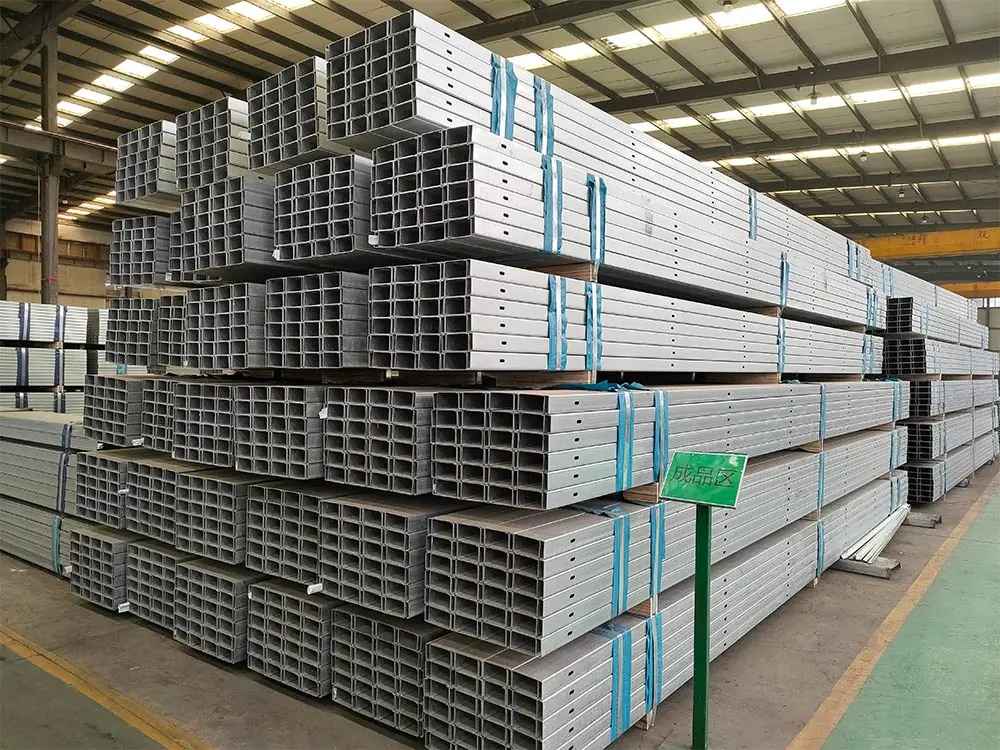

Основные особенности и структурные преимущества
С-образная сталь предлагает высокое соотношение прочности и веса и простую установку. Его открытый канал позволяет легко выравнивать болты и быстро собирать, сохраняя жесткость для коротких и средних промежутков. Процесс рулонообразования сохраняет размеры точными и последовательными в больших партиях.
Ключевые характеристики C-профилей
- Диапазон толщины: 1,5 – 3,0 мм
- Прочность: ≥ 350 МПа
- Отличная совместимость с горячим оцинкованием или покрытиями Zn-Al-Mg
- Идеально подходит как для вертикальных, так и для горизонтальных нагрузок
Параметр Типичный диапазон Инженерные преимущества
| Параметр | Типичный диапазон | Инженерные преимущества |
| Плотность | Низкий | Легкая обработка и транспортировка |
| Торсионная жесткость | Средний | Требует крепления для длинных расстояний |
| Защита от коррозии | HDG / Зн-Аль-Мг | 20-30 лет на открытом воздухе |
| Типичное использование | Крышевые крепления, рельсы | Легкая интеграция |
Лучшие приложения в фотоэлектрических стойках и промышленных опорах
С-профили широко используются в системах монтажа крыши, подрельсах и легких промышленных опорах. Их равномерная форма упрощает выравнивание на месте и минимизирует ошибки установки.
Ограничения, которые следует учитывать при использовании сечения
Цезарианские сечения могут крутиться под эксцентричными или длительными нагрузками, если не надлежащим образом укреплены. Для длинных просторов или зон с высоким крутением, таких как карпорты, инженеры часто заменяют или укрепляют их Z- или H-секциями для поддержания конструктивной жесткости.
Z-профильная сталь: для оптимизации напряжения и нагрузки
Уникальная геометрия и распределение прочности
Z Стальной канал оснащены смещенными фланцами, которые позволяют перекрываться на соединениях, создавая непрерывные расстояния с повышенным сопротивлением изгибу. Эта геометрия распределяет напряжение равномерно и улучшает производительность в больших приложениях. Профили также эффективно укладываются во время отгрузки, снижая объем грузов почти на 40 процентов.
Общее использование в солнечных карпортах и системах purlin
В солнечных карпортах и сельскохозяйственных крышах Z-профили служат первичными воротами, соединяющими конструктивные колонны. Перекрывающаяся конструкция обеспечивает жесткость к боковому давлению ветра, сохраняя при этом общий вес умеренным.
CZT Z-Profile Carport Beam (CZT-Z Series) предназначен для модульных конструкций карпортов. Производится на точных линиях рулонообразования и покрыт сплавом Zn-Al-Mg, он соответствует европейским стандартам EN 1993 и AS / NZS 4600 для нагрузки и коррозии. Результатом является длительный срок службы как в прибрежном, так и в засушливом климате.
Z-профили сочетают в себе легкую обработку из царевских сечений с конструктивной непрерывностью более тяжелых лучей, что делает их идеальным профилем для средних и больших установок, где эффективность должна обеспечиваться без бесполезной массы.
H-Beam и H-Section Steel для тяжелых конструкций
Широкофланцевая конструкция и несущая способность
H-образная сталь обычно называется широкофланцевой сталью. Он обеспечивает максимальное сопротивление изгибу и сдвигу в стандартном профиле. Из-за своей симметрии нагрузки распределяются равномерно по обоим фланцам и сетке, которая может поддерживать вертикальные, боковые и крутящие силы.
H-секции стали незаменимыми для наземных солнечных батарей, крыш складов и больших фундаментов карпортов из-за их жесткости и стабильности размеров при нагрузках снега или сейсмической активности.
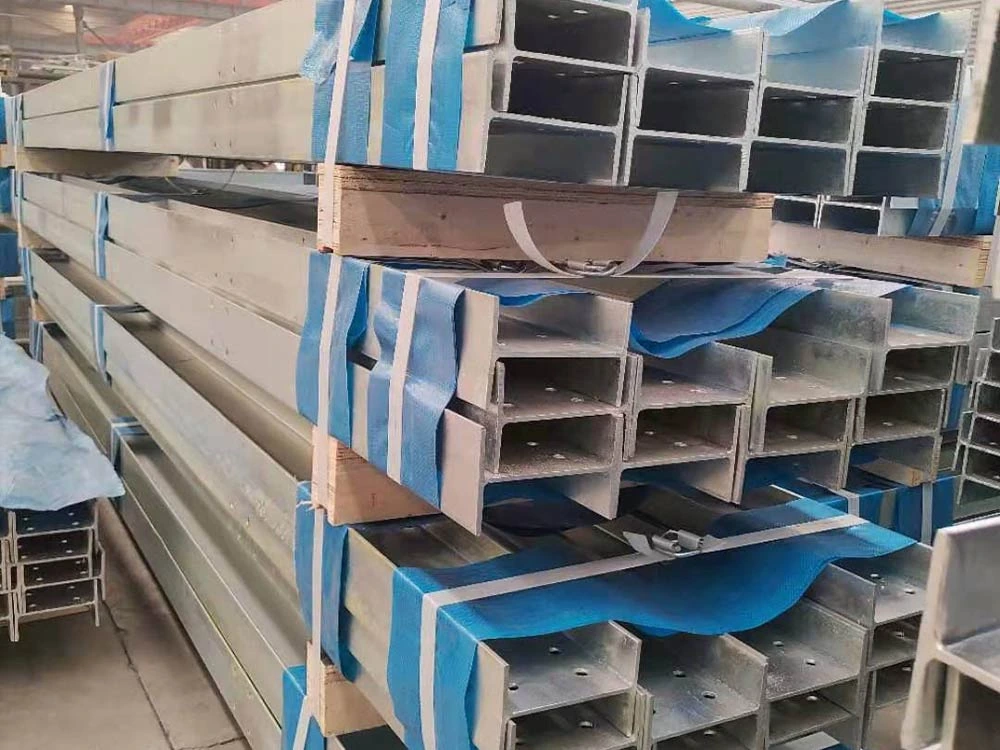

Когда выбрать H-секции над Z или C
- H-секции предпочтительны, когда проекты требуют:
- Очень высокая осиевая и гибкая прочность
- Большие проширения или глубокие фундаменты
- Снижение вибрации и отклонения при динамической нагрузке
Расходы и соображения по изготовлению
H-профили используют больше стали и требуют более тяжелой транспортировки, но они резко сокращают долгосрочное обслуживание. В течение 25-летнего срока службы их долговечность компенсирует более высокие первоначальные затраты на материалы, особенно для проектов, подверженных экстремальным погодным условиям.
Как выбрать правильную стальную форму для вашего проекта
Критерии отбора: нагрузка, диапазон, установка, окружающая среда
Выбор правильного профиля предполагает оценку как структурных, так и специфических факторов. Инженеры обычно считают:
- Тип нагрузки: статический (снег, панели) против динамического (ветер, сейсмический)
- Длина расстояния: Секции Z или H, рекомендуемые для диапазонов > 6 м
- Воздействие коррозии: Покрытия Zn-Al-Mg для прибрежного или влажного климата
- Простота установки: С-профили предпочтительны для крыш или небольших проектов
Таблица сравнения: профиль C vs Z vs H
| Критерии | C-профиль | Z-профиль | H-профиль |
| Подшипник нагрузки | Средний | Высокий | Очень высокий |
| Расширение диапазона | короткий - средний | Длинный | Очень длинный |
| Вес | Свет | Умеренный | Тяжелые |
| Эффективность затрат | Высокий | Средний | Средний - Низкий |
| Идеальное использование | Крыша / Подрельс | Carport / Трекер | Земля / Фонд |
Практические примеры солнечных монтажных проектов
На недавних установках в Юго-Восточной Азии, управляемых CZT, гибридные системы с использованием C-профилей для верхних рельсов, Z-профилей для средних перлин и H-балок для базовых колонн снизили общий вес стали на 10-15 процентов, сохраняя при этом соответствие местным ветровым кодексам.
Для коммерческого проекта крыши на Филиппинах компания применила кесаревские сечения для упрощения транспортировки и сборки. Работники завершили массив мощностью 1 МВт менее чем за три недели, что свидетельствует о том, что оптимизированный выбор профиля сокращает время установки и улучшает доходность инвестиций.
CZT’ экспертизы в области проектирования и производства стальных профилей
Интеграция профилей C, Z и H в солнечные конструкции
CZT интегрирует несколько типов профилей в одну сплоченную систему для сбалансированной стоимости и производительности. Профили C и Z обеспечивают регулируемость и быструю сборку, в то время как H-балки укрепляют фиксированные фундаменты. Эта модульная конструкция обеспечивает последовательные пути нагрузки и упрощает логистику для EPC и партнеров по разработке по всему миру.
Передовые решения для покрытий и защиты от коррозии
Компания применяет передовые Zn-Al-Mg и горяче оцинкованные покрытия для обеспечения ведущей в своем классе устойчивости к окислению и абразии. Эти покрытия соответствуют требованиям стандартов ISO 1461, ASTM A123 и ASTM B117 для соляного распыления и работают более 25 лет, даже в высоковлажных или прибрежных зонах.
Почему глобальные клиенты выбирают CZT для проектов стальных конструкций
CZT предоставляет собственное производство, заказную инженерию и поддержку проектов под ключ клиентам по всему миру. Поставляя более 3 ГВт монтажных конструкций в более чем 50 стран, компания гарантирует, что все ее продукты соответствуют европейским, австралийским и японским стандартам конструкции. Его линейки продуктов включают серии CZT-C, CZT-Z и CZT-H для применения от легких крыш до крупномасштабных солнечных ферм.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
В: В чем главное различие между стальными профилами C, Z и H?
А: С-профили легкие и просты в установке для крыш и небольших рам. Z-профили перекрываются, чтобы эффективно сформировать более длинные расстояния. H-профили обеспечивают максимальную прочность для наземных или тяжелых промышленных конструкций.
В: Какой стальный профиль лучше всего работает для солнечных карпортов?
А: Z-профили, как правило, идеально подходят для карпортов, потому что их геометрия поддерживает длинные расстояния с меньшим количеством соединений. Для многослойных или ветровых карпортов система CZT H-Beam предлагает превосходную жесткость.
В: Как покрытия влияют на срок службы стальных профилей?
А: Защитные покрытия, такие как горячее оцинкование и сплав Zn-Al-Mg, предотвращают ржавчину и износ поверхности. CZT применяет оба метода для обеспечения 25-30 лет надежного обслуживания на открытом воздухе.
В: Можно ли объединить различные типы профилей в одном проекте?
А: - Да. - Да. Многие крупные фотоэлектрические системы смешивают профили - C для рельсов, Z для порок и H для колонн - для сбалансирования стоимости, веса и конструктивной прочности. CZT’ модульные системы предназначены для таких гибридных конфигураций.
Q: Кто производит надежные стальные профили C, Z и H для солнечных конструкций?
А: CZT, базирующаяся в Тяньцзине, Китай, разрабатывает и производит высококачественные монтажные системы с использованием стальных профилей C, Z и H. Сертифицированная по ISO 9001 и ISO 1461, компания обеспечивает последовательное качество и своевременное поставку для глобальных солнечных проектов.